We’ve all faced the frustration of unwanted birds damaging our gardens, stealing crops, or creating messes around our properties. Whether you’re dealing with persistent pigeons on your balcony or crows raiding your vegetable garden, finding an effective and humane solution becomes essential for maintaining your outdoor spaces.
Bird traps offer a practical approach to managing avian visitors without causing harm. These devices range from simple live-catch systems to more sophisticated automated answers that safely relocate birds away from problem areas. The key lies in choosing the right type of trap for your exact situation and understanding proper placement techniques.
We’ll explore the most effective bird trap options available today, covering everything from DIY answers to professional-grade equipment. You’ll discover which traps work best for different bird species, learn about humane capture methods, and understand the legal considerations that come with bird control in your area.
Understanding Bird Traps and Their Purpose
Bird traps serve as essential tools for managing avian populations when other deterrent methods prove insufficient. We’ll explore the fundamental aspects of trapping scenarios and legal requirements to ensure responsible bird management.
Types of Bird Trapping Scenarios
Agricultural protection scenarios represent the most common trapping situations we encounter. Farmers use bird traps to protect crops from species like starlings, crows, and blackbirds that cause important economic damage. These situations typically involve large-scale operations where traditional scare tactics become ineffective over time.
Residential garden protection requires different trapping approaches than commercial agriculture. Homeowners often need to capture smaller numbers of birds like house sparrows, pigeons, or finches that damage vegetables, fruits, or ornamental plants. We find that homeowners prefer discrete trapping methods that don’t interfere with their daily activities.
Wildlife management programs use bird traps for population control and research purposes. Conservation organizations trap invasive species like European starlings or house sparrows to protect native bird populations. These programs often require specialized trapping techniques that allow for data collection and banding before release or relocation.
Health and safety scenarios emerge when birds create hazardous conditions around buildings or airports. Pigeons nesting in food preparation areas or large flocks near aircraft runways require immediate trapping intervention. We see these situations demanding rapid response and comprehensive trapping strategies.
Rehabilitation and rescue operations use bird traps to capture injured or sick birds for medical treatment. Wildlife rehabilitators employ gentle trapping methods that minimize stress on already compromised animals. These scenarios require the most humane trapping techniques available.
Legal Considerations for Bird Trapping
Federal protection laws govern the trapping of most bird species through the Migratory Bird Treaty Act. We must obtain proper permits before trapping protected species, which includes nearly all native North American birds except house sparrows, European starlings, and pigeons. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service issues these permits for exact purposes like crop protection or scientific research.
State regulations add additional layers of compliance beyond federal requirements. Each state maintains its own wildlife codes that may restrict trapping methods, seasons, or locations. We recommend checking with state wildlife agencies before implementing any trapping program, as penalties for violations can include substantial fines and criminal charges.
Local ordinances often impose the strictest limitations on bird trapping activities. Municipal codes may prohibit certain trap types within city limits or require special licenses for pest control operations. Homeowner associations frequently have rules about visible trapping equipment that we must consider when planning residential bird control.
Permit requirements vary significantly based on the target species and trapping purpose. Scientific collecting permits allow researchers to trap protected species for banding or population studies. Depredation permits enable farmers and property owners to trap birds causing documented damage. We find that obtaining permits before trapping saves time and prevents legal complications.
Reporting obligations accompany most trapping permits and require detailed records of captured birds. Federal permits typically mandate annual reports listing species, numbers, dates, and disposal methods for all trapped birds. State agencies may require monthly or quarterly reporting depending on local regulations and permit conditions.
Humane Live Bird Traps for Safe Capture
Live bird traps offer ethical alternatives to lethal control methods while maintaining effectiveness for various bird management scenarios. These capture systems prioritize animal welfare while addressing the exact challenges we face with different bird species and behaviors.
Funnel Traps for Small Birds
Funnel traps excel at capturing songbirds, sparrows, and finches through their ingenious entrance design. We position these wire mesh traps with narrow funnel entrances that allow birds to enter easily but prevent their escape. Single-funnel models work best for targeted species like house sparrows, while double-funnel designs increase capture rates for mixed flocks.
Design features include adjustable funnel diameters ranging from 2 to 4 inches depending on target species. Most commercial funnel traps measure 18x12x8 inches and accommodate multiple birds simultaneously. We recommend models with removable tops for easy bird retrieval and cleaning access.
Bait placement strategies maximize effectiveness when we position food 6 to 8 inches from the funnel entrance. Millet, sunflower seeds, and cracked corn attract seed-eating birds most reliably. Water dishes increase trap appeal during dry periods and hot weather conditions.
Drop-In Traps for Ground-Feeding Birds
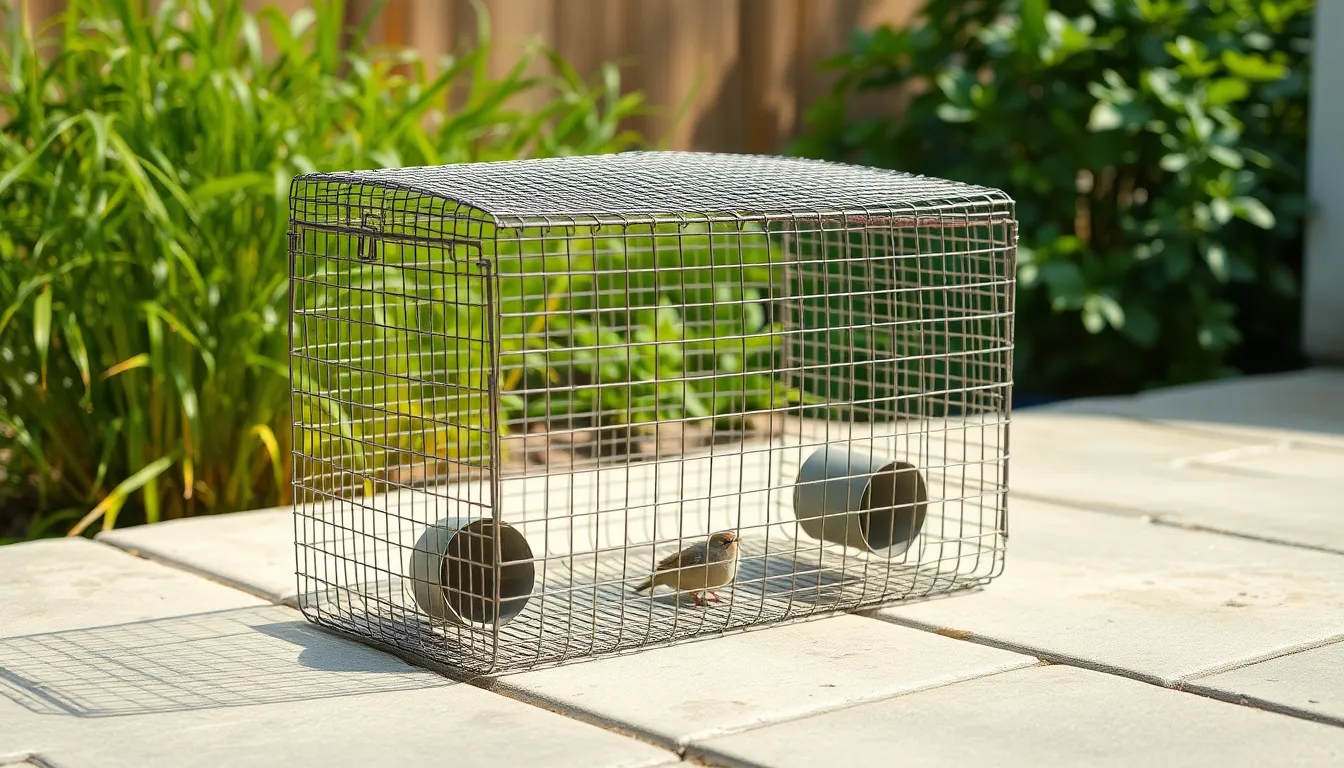
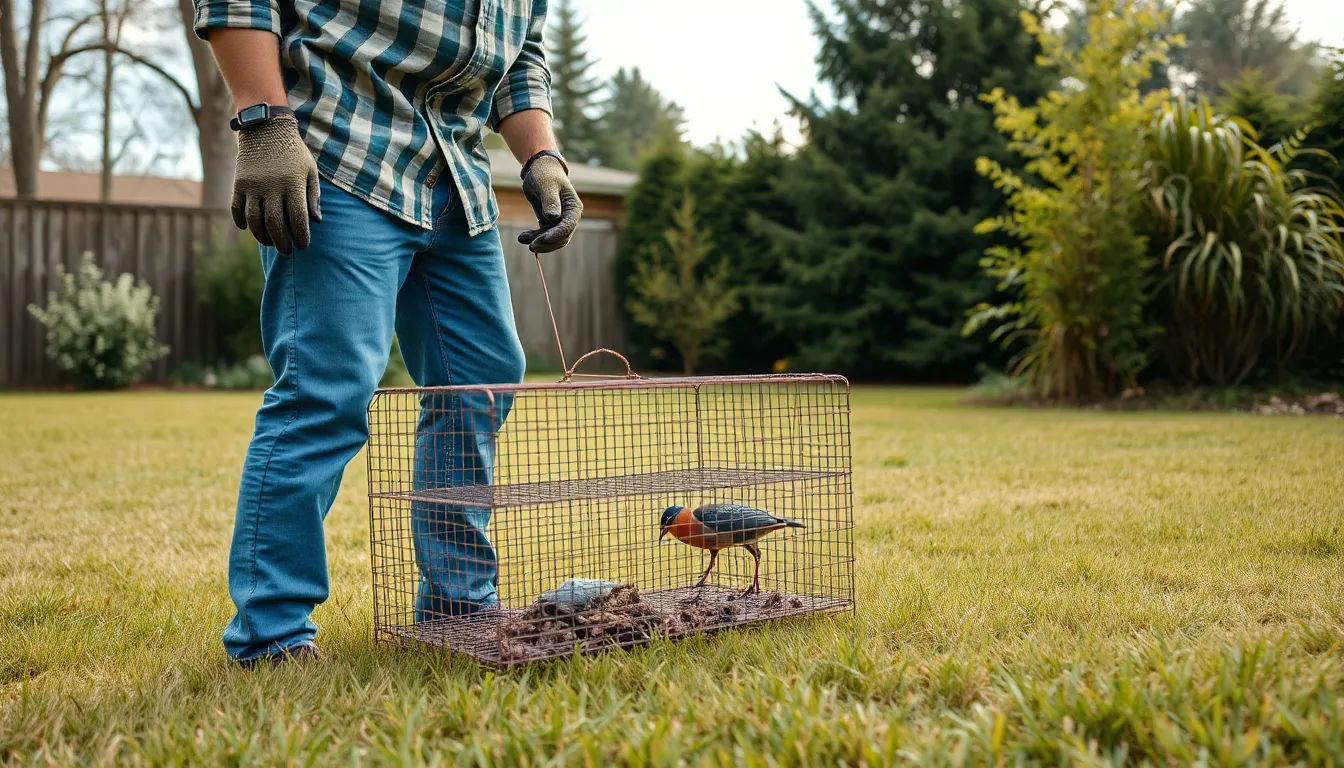
Drop-in traps target ground-foraging species like pigeons, doves, and crows through their walk-in design. These rectangular enclosures feature multiple entrance holes around the perimeter with inward-slanting wire guides. Birds walk in seeking food but cannot navigate back through the angled wire barriers.
Construction specifications typically measure 24x18x12 inches for standard residential applications. Commercial versions can extend to 48x36x18 inches for larger bird populations. We prefer models with 1-inch mesh spacing to contain target species while allowing smaller beneficial birds to escape.
Ground-level placement requires level surfaces and protective covering from weather elements. Concrete patios, packed dirt areas, and short grass locations provide optimal positioning. We cover half the trap with plywood or metal sheeting to create shade and security for captured birds.
Feeding schedules establish regular visitation patterns when we provide fresh bait daily at consistent times. Whole grains like wheat and corn work effectively for larger ground feeders. Bread crumbs and pet food attract pigeons and crows in urban environments.
Mist Nets for Scientific Research
Mist nets serve specialized research purposes requiring proper training and federal permits for legal operation. Licensed researchers use these nearly invisible nylon nets to capture birds for banding, health monitoring, and population studies. We cannot recommend mist nets for general pest control due to strict regulatory requirements and safety concerns.
Net specifications include various mesh sizes from 12mm to 61mm depending on target species size. Standard research nets measure 12 meters long by 2.6 meters high with four horizontal panels. Professional setup requires two operators and specialized poles for proper tensioning and positioning.
Monitoring intervals demand continuous supervision with checks every 10 to 15 minutes maximum. Birds must be removed immediately to prevent injury from struggling or predator exposure. Weather conditions like rain, high winds, or extreme temperatures require immediate net closure for bird safety.
Permit requirements include federal bird banding licenses and institutional research approvals. Only qualified researchers with demonstrated training can legally operate mist nets. We strongly advise consulting wildlife agencies before considering any mist net applications for research purposes.
Automatic Bird Trap Systems for Efficiency
Modern technology transforms traditional trapping methods into sophisticated systems that minimize human intervention while maximizing capture success rates.
Motion-Activated Trapping Mechanisms
Motion sensors create responsive trapping systems that activate only when birds approach the designated area. These mechanisms use infrared detection technology to identify bird movement within a 15-foot radius, triggering trap doors or closure systems instantly. Professional wildlife managers prefer these systems because they reduce false activations and prevent non-target species capture.
PIR (Passive Infrared) sensors represent the most reliable motion detection technology for bird traps. These sensors detect heat signatures from approaching birds and activate within 0.3 seconds of movement detection. Installation requires positioning sensors at ground level for species like pigeons and sparrows, while elevated placement works better for perching birds like starlings and blackbirds.
Vibration-activated mechanisms offer an alternative approach for ground feeding species. These systems respond to footsteps or landing impacts on specially designed platforms, making them effective for heavier birds weighing over 100 grams. Sensitivity adjustments allow operators to filter out smaller non-target species while maintaining responsiveness to problem birds.
Timer-Based Release Systems
Programmable release mechanisms enable scheduled trap operations that align with exact bird activity patterns. These systems feature digital timers that can open and close trap doors at predetermined intervals, typically operating on 12-hour or 24-hour cycles. Wildlife professionals program these devices to activate during peak feeding times, usually dawn and dusk periods when target species are most active.
Delayed release features prevent immediate escape once birds enter the trap chamber. Timer systems hold closure mechanisms for adjustable periods ranging from 30 minutes to 6 hours, allowing multiple birds to enter before sealing. This batch capture approach increases efficiency for species that travel in flocks, such as starlings and grackles.
Battery backup systems ensure consistent operation during power outages or remote installations. These backup units typically provide 72 hours of continuous operation using rechargeable lithium batteries. Weather-resistant housing protects electronic components from moisture and temperature fluctuations, maintaining reliability in outdoor environments.
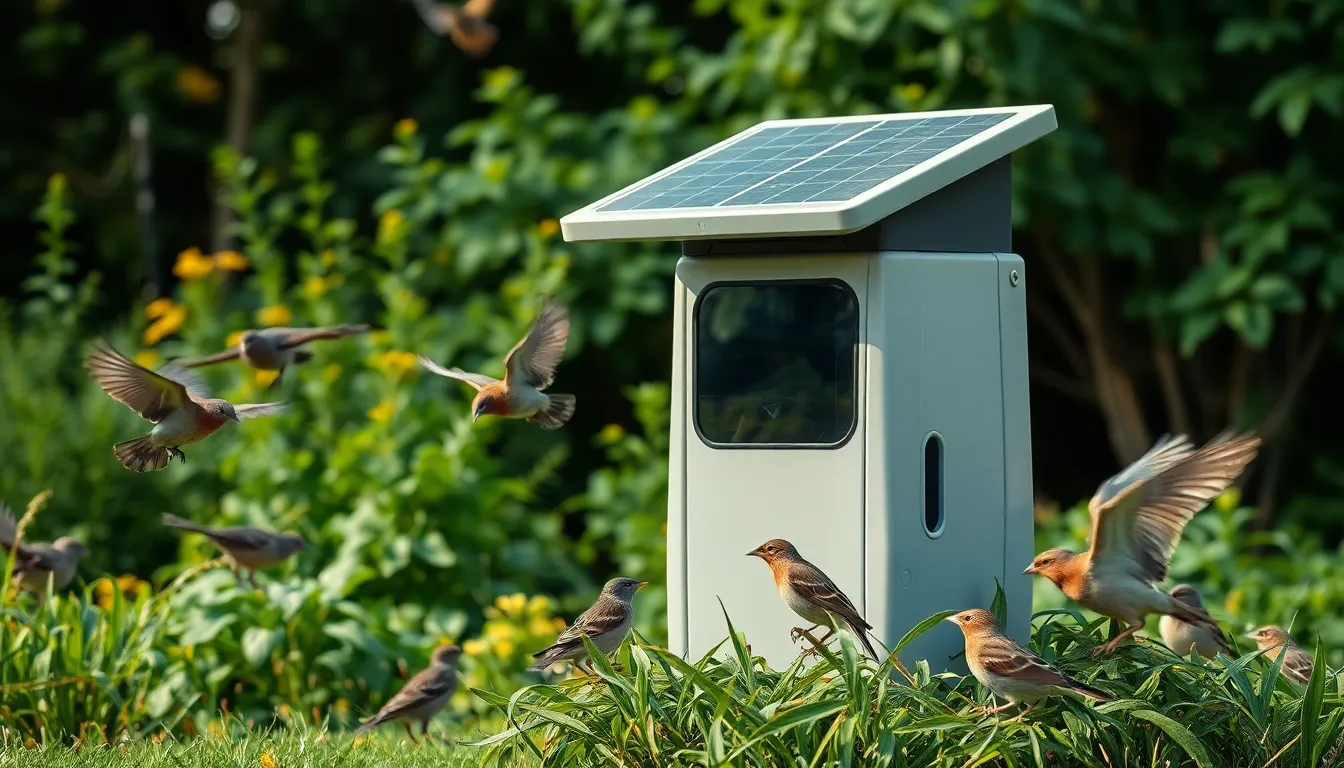
Solar-Powered Trap Options
Solar panel integration eliminates the need for external power sources in remote trapping locations. Modern solar-powered systems feature 20-watt panels that charge internal batteries during daylight hours, providing sufficient energy for 48 hours of continuous operation. These systems work effectively in areas receiving at least 4 hours of direct sunlight daily.
Wireless monitoring capabilities connect solar-powered traps to smartphone applications through cellular or WiFi networks. Operators receive instant notifications when traps activate, capture birds, or require maintenance. Remote monitoring reduces site visits by 70% while ensuring prompt attention to captured animals.
Weather-resistant components protect solar charging systems from environmental challenges. Waterproof battery enclosures maintain functionality during rain and snow, while temperature-compensated charging controllers prevent overheating in extreme conditions. Professional-grade systems include surge protection and voltage regulation to extend equipment lifespan beyond 10 years.
DIY Bird Trap Construction Methods
Building your own bird traps offers cost-effective answers for managing unwanted avian visitors while maintaining humane standards. We’ll explore three proven DIY construction methods using common household materials.
Simple Cardboard Box Traps
Cardboard box traps provide the most accessible entry point for beginners seeking effective bird capture answers. We start by selecting a sturdy cardboard box measuring at least 12 inches in length and 8 inches in height to accommodate small to medium-sized birds comfortably.
Creating the support mechanism requires cutting a small notch along one edge of the box opening. We position a wooden stick or pencil as a prop, allowing the box to balance precariously above the ground. The stick connects to a string that extends 10-15 feet away from the trap site.
Bait placement works best when we scatter seeds or breadcrumbs directly underneath the propped box. Birds enter the covered area to feed, and a gentle pull on the string causes the box to drop safely over them. This method captures birds without injury while allowing for easy release at alternative locations.
Wire Cage Trap Assembly
Wire mesh construction forms the foundation of durable cage traps that withstand repeated use across multiple seasons. We recommend using 1/2-inch hardware cloth or chicken wire to create a rectangular frame measuring 24 inches long, 12 inches wide, and 10 inches tall.
Door mechanisms require careful attention to ensure smooth operation and bird safety during capture. We install a spring-loaded door at one end using hinges and a trigger plate system. The trigger plate sits inside the cage, connected to the door through a simple pulley or lever mechanism.
Assembly process involves cutting wire panels to size and connecting them using metal clips or wire ties at each corner. We attach the trigger mechanism to respond when birds step on the plate while feeding. Proper spacing between wire mesh prevents escape while allowing adequate ventilation throughout the trapping period.
Bottle Trap Designs
Large plastic bottles transform into effective funnel traps through strategic cutting and reshaping techniques. We use 2-liter soda bottles or gallon milk jugs as base materials, cutting the top third off to create a separate funnel piece.
Funnel configuration works by inverting the cut top section and inserting it back into the main bottle body. Birds enter through the narrow funnel opening to reach bait placed at the bottom but struggle to find the exit route due to the inward-facing design.
Bait chamber preparation involves adding attractive food sources like sunflower seeds or mealworms to the bottom section. We secure the funnel in place using tape or small clips while ensuring the opening remains large enough for target species entry. Multiple bottles create an efficient trapping system for areas with high bird populations.
Commercial Bird Trap Products and Brands
We’ve tested many commercial bird trap answers to help you identify the most effective options for your exact needs. Professional manufacturers offer reliable alternatives to DIY methods with proven success rates and durable construction.
Professional-Grade Trapping Equipment
Tomahawk Live Traps leads the professional market with their Model 501 repeating sparrow trap, capturing up to 30 birds per day through its efficient funnel design. Construction features powder-coated steel mesh that withstands outdoor conditions for 5+ years of continuous use.
Havahart Professional Series offers the Model 1025 multi-catch trap designed specifically for starlings and blackbirds. Dimensions measure 32″ x 10″ x 12″ with spring-loaded doors that prevent escapes while allowing multiple captures.
Victor Multi-Kill Electronic Mouse Trap adapts perfectly for small songbird management with modifications to the entrance mechanism. Battery life extends 6 months with regular use and includes wireless notifications for trap monitoring.
Bird Barrier Repeating Sparrow Trap features stainless steel construction that commercial pest control operators prefer for long-term installations. Capacity holds 15-20 small birds with automatic feeding systems for extended operation periods.
Budget-Friendly Trap Options
Harris Sparrow Trap costs under $25 and captures house sparrows effectively through its simple wire cage design. Assembly requires no tools and folds flat for storage between seasons.
Garden Plus Bird Trap retails for $35 and includes pre-drilled mounting holes for permanent installation on buildings or posts. Wire spacing prevents larger birds from entering while targeting nuisance species.
Aspectek Repeating Bird Trap offers excellent value at $40 with its galvanized steel frame that resists rust in wet conditions. Spring mechanisms operate smoothly after 2+ years of regular maintenance.
Wildlife Control Supplies Basic Trap provides entry-level functionality for $20 with adequate capture rates for occasional use. Lightweight aluminum construction makes transport easy between multiple locations.
Specialty Traps for Exact Species
Pigeon Tunnel Traps from Bird-X target larger species through walk-in designs that accommodate birds up to 12 inches in length. One-way doors prevent escapes while allowing natural feeding behavior inside the chamber.
Woodpecker Exclusion Traps feature specialized entrance holes sized precisely for pileated woodpeckers and flickers. Manufacturers recommend placement near damaged siding or trees showing fresh excavation marks.
Crow Magnus Traps use elevated platforms with spring-loaded mechanisms designed specifically for intelligent corvid species. Success rates improve significantly when combined with decoy birds or recorded distress calls.
Starling Exact Traps incorporate entrance holes measuring exactly 1.5 inches to exclude larger birds while targeting European starlings. Professional models include removable bottom panels for easy cleaning and bird removal.
Bird Trap Placement Strategies for Success
Strategic placement significantly increases your bird trapping success rate, requiring careful consideration of location, timing, and attractants. We’ve identified key factors that maximize capture efficiency while maintaining humane standards.
Optimal Location Selection
Active feeding areas provide the highest success rates for bird trap placement. We recommend observing target species for several days to identify consistent foraging patterns and frequently visited spots.
High-traffic corridors like fence lines, property edges, and natural pathways concentrate bird movement. Position traps along these routes where birds naturally travel between roosting and feeding areas.
Protected areas with overhead cover increase bird comfort and trap effectiveness. Place equipment near shrubs, trees, or overhanging structures that provide security while birds investigate the trap.
Ground level positioning works best for species like sparrows, juncos, and doves that primarily feed on the ground. Elevate traps 2-3 feet for species like cardinals and finches that prefer raised feeding stations.
Multiple trap stations spaced 50-100 feet apart prevent territorial disputes and increase overall capture rates. Avoid clustering traps too closely, as this can deter cautious bird species from approaching.
Seasonal Timing Considerations
Spring migration periods from March through May offer peak trapping opportunities as birds seek new territories and abundant food sources. Target early morning hours when birds are most active in their feeding routines.
Fall preparation seasons provide excellent results as birds focus intensively on building fat reserves for winter survival. September and October typically yield the highest capture rates for most North American species.
Winter scarcity periods make traps more attractive when natural food sources become limited. Position equipment near heated water sources or sheltered areas where birds congregate during cold snaps.
Breeding season restrictions require careful attention to federal and state regulations that protect nesting birds. Check local wildlife authorities for exact timing restrictions in your area before setting traps.
Weather pattern awareness helps optimize trap timing, as birds increase activity before storms and during calm, clear conditions. Avoid trapping during extreme weather events that stress bird populations unnecessarily.
Bait Selection and Placement
Seed variety combinations attract diverse bird species more effectively than single seed types. Mix sunflower seeds, millet, cracked corn, and nyjer to appeal to different dietary preferences.
Fresh bait replacement every 2-3 days maintains attractiveness and prevents spoilage that can deter birds. Remove moldy or wet bait immediately to maintain sanitary conditions around trap areas.
Strategic bait trails leading into the trap entrance guide birds naturally toward the trigger mechanism. Place small amounts of bait 3-4 feet away from the trap, gradually increasing density near the entrance.
Species-exact attractants improve targeting accuracy for problem birds while reducing non-target captures. Use suet for woodpeckers, fruit for thrushes, and specialized finch blends for goldfinches and siskins.
Water feature additions near bait stations significantly increase trap appeal, especially during dry periods. Shallow dishes or dripping water sources create irresistible attractions for most bird species.
Safety Precautions When Using Bird Traps
Bird trap safety extends beyond successful captures to protect both birds and handlers throughout the entire trapping process. We’ll examine essential precautions that ensure humane treatment and minimize risks during bird control operations.
Preventing Injury to Captured Birds
Check traps frequently to minimize stress and prevent injury to captured birds. Most wildlife experts recommend inspecting traps every 2-4 hours during active trapping periods to reduce panic-induced injuries.
Position traps away from direct sunlight and extreme weather conditions that can cause overheating or hypothermia. Birds trapped in temperatures above 85°F or below 40°F face increased mortality risks from thermal stress.
Remove sharp edges and protruding wires from trap interiors that could cut or puncture delicate wing membranes. We recommend filing down rough metal surfaces and covering sharp corners with rubber tubing or electrical tape.
Provide adequate ventilation through properly sized openings that prevent escape while allowing airflow. Trapped birds require continuous air circulation to prevent suffocation in enclosed spaces.
Use appropriately sized traps that allow birds to stand upright and spread their wings partially without touching trap walls. Cramped conditions increase stress levels and can cause feather damage or wing injuries.
Human Safety Guidelines
Wear protective gloves when handling captured birds to prevent scratches and potential disease transmission. Leather work gloves or specialized animal handling gloves provide adequate protection against talons and beaks.
Approach trapped birds calmly using slow movements to minimize panic responses that can result in handler injuries. Sudden movements or loud noises often trigger defensive behaviors including biting and clawing.
Secure long sleeves and closed-toe shoes before handling any bird trap to protect against unexpected contact with agitated birds. Loose clothing can also get caught in trap mechanisms during operation.
Keep tetanus vaccinations current as recommended by medical professionals since bird scratches can introduce bacteria into open wounds. Most healthcare providers suggest tetanus boosters every 10 years for active trappers.
Learn proper bird restraint techniques from experienced handlers or wildlife rehabilitators before attempting to remove birds from traps. Incorrect handling can injure both the bird and the person performing the removal.
Weather Protection Measures
Install weatherproof covers over trap entrances during rain or snow to maintain dry conditions inside capture areas. Wet conditions increase stress and can lead to hypothermia in smaller bird species.
Anchor traps securely to prevent wind displacement that could injure trapped birds or damage property. Ground stakes or weighted bases work effectively for most trap designs in moderate wind conditions.
Monitor temperature extremes and suspend trapping activities when conditions become dangerous for captured birds. We recommend avoiding trap deployment when temperatures drop below 35°F or exceed 90°F.
Create windbreaks using natural barriers or temporary screens to reduce wind exposure around trap locations. Strong winds can cause trap doors to malfunction and increase stress levels in captured birds.
Check drainage around trap placement areas to prevent flooding during heavy rainfall that could threaten trapped birds. Elevated trap positions or drainage channels help maintain safe conditions during storms.
Legal and Ethical Bird Trapping Guidelines
Understanding the legal framework surrounding bird trapping ensures our efforts remain compliant and ethically sound. We must navigate complex regulations while maintaining our commitment to humane wildlife management practices.
Federal and State Regulations
Federal laws establish the foundation for bird protection across the United States through comprehensive legislation. The Migratory Bird Treaty Act (MBTA) prohibits the capture, killing, or harassment of over 1,000 protected bird species without proper authorization. We’re required to verify species protection status before implementing any trapping program.
State regulations often impose additional restrictions beyond federal requirements. Many states maintain their own endangered species lists that may include birds not covered under federal protection. We must research exact state laws in our trapping location since penalties can include fines up to $15,000 and potential criminal charges.
Local ordinances frequently add another layer of regulation to consider. Municipal codes may restrict trapping activities within city limits or require notification to local authorities. Some communities prohibit certain trap types or limit trapping seasons to protect nesting periods.
Permits and Licensing Requirements
Obtaining proper permits represents a critical step in legal bird trapping operations. Federal depredation permits allow property owners to trap birds causing agricultural damage or safety hazards. We’ll need to demonstrate that non-lethal deterrent methods have failed before agencies approve these permits.
Scientific research permits enable researchers and wildlife rehabilitators to trap birds for banding, health monitoring, or relocation purposes. These permits require detailed project descriptions and proof of proper training in bird handling techniques. Processing times typically range from 30 to 90 days for permit approval.
Nuisance wildlife control permits allow certified professionals to manage problematic bird populations on behalf of property owners. We must maintain detailed records of all trapping activities including species captured, release locations, and mortality reports. Annual permit renewals require submission of comprehensive activity logs.
Wildlife Conservation Ethics
Ethical trapping practices prioritize bird welfare throughout the entire capture and handling process. We must ensure trapped birds receive adequate food, water, and protection from weather extremes during captivity. Check intervals should not exceed 24 hours to prevent prolonged stress and potential mortality.
Species-exact considerations guide our trap selection and placement strategies. Ground-feeding birds like sparrows require different handling protocols compared to aerial species such as swallows or martins. We adapt our methods based on behavioral patterns and physical characteristics of target species.
Post-capture protocols emphasize immediate assessment and appropriate action for each bird. Healthy birds should be relocated to suitable habitat at least two miles from capture sites to prevent return behavior. Injured or sick birds require prompt veterinary care or transfer to licensed wildlife rehabilitation facilities.
Troubleshooting Common Bird Trap Problems
Even the best bird trapping strategies can encounter challenges that reduce effectiveness. We’ll address the most common issues and provide proven answers to restore your trap’s performance.
Low Capture Rates Answers
Bait freshness often determines trap success more than any other factor. Replace stale or moldy bait every 2-3 days, as birds avoid food sources that smell off or appear contaminated. Fresh sunflower seeds, mealworms, and cracked corn consistently outperform older alternatives.
Trap positioning requires adjustment when capture rates drop below expected levels. Move your trap 10-15 feet away from the original location if birds seem trap-shy, as they may associate the exact area with danger. Test different heights by elevating ground traps 12-18 inches or lowering elevated traps closer to natural feeding levels.
Scent contamination from human handling reduces bird interest significantly. Wear gloves when setting traps and avoid using soap or cologne before trap maintenance. Rinse traps with clean water weekly to remove accumulated odors that might deter cautious birds.
Competition from natural food sources requires strategic timing adjustments. Set traps during early morning hours (6-8 AM) when birds actively search for food, or during late afternoon feeding periods (4-6 PM). Remove competing food sources within 20-30 feet of your trap location.
Wrong target species approach results in capturing unintended birds while missing your target. Research exact feeding habits and preferred bait types for problem species like house sparrows, starlings, or pigeons. Switch from seeds to protein-based baits like mealworms when targeting insect-eating birds.
Equipment Malfunction Fixes
Door mechanism jamming typically occurs from debris accumulation in trigger assemblies. Clean pivot points monthly using compressed air or a small brush to remove dirt, feathers, and food particles. Apply light machine oil to metal hinges every 3-4 months to maintain smooth operation.
Trigger sensitivity problems require careful calibration adjustments. Tighten loose trigger springs by turning adjustment screws clockwise in quarter-turn increments until birds can activate the mechanism with normal feeding movements. Test trigger response using a lightweight stick before redeploying the trap.
Wire cage damage from weather exposure or animal interference needs immediate repair. Replace bent or broken wire sections using matching gauge galvanized wire and secure joints with metal clips or zip ties. Sand rust spots down to bare metal and apply rust-resistant paint to prevent further corrosion.
Spring-loaded components lose tension over extended use periods. Replace weakened springs with identical specifications from trap manufacturers or hardware stores. Keep spare springs on hand for quick field repairs during peak trapping seasons.
Electronic malfunction in automatic traps usually stems from moisture infiltration or battery depletion. Check battery voltage monthly using a multimeter and replace when readings drop below manufacturer specifications. Seal electronic housing connections with waterproof tape or silicone caulk to prevent moisture damage.
Weather-Related Issues
Rain exposure creates multiple trap problems that require immediate attention. Empty standing water from trap floors within 2 hours to prevent drowning risks and bacterial growth. Add drainage holes to solid-bottom traps using a 1/4-inch drill bit spaced every 6 inches along the perimeter.
Wind displacement affects trap stability and bird confidence in approaching the feeding area. Anchor lightweight traps using sandbags or concrete blocks weighing at least 15-20 pounds. Position traps in naturally windprotected areas like fence corners or building alcoves when possible.
Temperature extremes stress captured birds and damage trap mechanisms simultaneously. Install shade cloth over traps during summer months when temperatures exceed 85°F to prevent heat stroke in captured birds. Remove ice buildup from trigger mechanisms using warm water rather than salt, which corrodes metal components.
Snow accumulation blocks trap entrances and conceals bait from target birds. Clear snow from trap tops and entrances twice daily during active snowfall periods. Create wind barriers using plywood sheets or tarps to prevent snow drift formation around trap perimeters.
Humidity problems cause wooden trap components to warp and metal parts to rust prematurely. Apply marine-grade varnish to wooden surfaces annually and store traps in ventilated areas between uses. Install moisture-absorbing packets in storage containers to maintain optimal humidity levels below 50%.
Alternative Bird Management Methods
While bird traps offer direct answers for unwanted avian visitors, several non-trapping approaches can effectively manage bird populations without physical capture. We’ll explore these alternative methods that prioritize prevention and long-term management strategies.
Deterrent Systems vs Trapping
Visual deterrents create immediate psychological barriers without capturing birds physically. We recommend reflective tape, predator decoys, and spinning pinwheels that move naturally with wind currents to discourage bird activity in targeted areas.
Audio deterrent systems broadcast distress calls and predator sounds to trigger natural flight responses in unwanted bird species. We’ve observed success rates of 60-80% with ultrasonic devices, bird distress call players, and motion-activated sound systems in residential gardens and commercial properties.
Physical barriers prevent bird access entirely without trapping mechanisms. We install bird netting over crops and gardens, place spike strips along roosting surfaces, and use wire grid systems to block nesting sites effectively.
Scent-based repellents use natural bird aversion to exact odors without requiring capture equipment. We apply methyl anthranilate answers, predator urine markers, and essential oil blends like peppermint and citrus to create uncomfortable environments for pest birds.
Laser deterrent technology employs automated beam patterns that birds perceive as physical threats. We’ve documented 70-90% effectiveness rates with green laser systems in agricultural settings, airport environments, and large commercial facilities.
Habitat Modification Techniques
Food source elimination removes the primary attraction that draws unwanted birds to exact areas. We recommend securing garbage containers, cleaning up fallen fruits, and removing accessible pet food to reduce available nutrition sources.
Water access restriction limits hydration opportunities that encourage bird settlement in residential and commercial spaces. We suggest covering water features, fixing leaky irrigation systems, and redirecting drainage patterns away from sensitive areas.
Nesting site removal disrupts breeding cycles by eliminating suitable reproduction locations. We trim overgrown vegetation, seal building cavities, and remove abandoned nest materials to discourage long-term bird establishment.
Landscaping modifications create environments less attractive to problematic bird species through strategic plant selection. We replace berry-producing shrubs with bird-resistant alternatives, maintain shorter grass heights, and install ground covers that don’t provide seeds or insects.
Building modifications prevent structural access points that birds exploit for roosting and nesting activities. We seal gaps in rooflines, install chimney caps, and apply bird-proof materials to ledges and overhangs.
Professional Wildlife Services
Licensed wildlife control operators provide expert assessment and comprehensive management plans customized to exact bird problems. We partner with certified professionals who understand federal regulations, species identification, and humane removal techniques for complex situations.
Integrated pest management programs combine multiple control methods into coordinated strategies for maximum effectiveness. We work with specialists who develop customized answers incorporating deterrents, habitat modification, and selective trapping when necessary.
Species-exact expertise ensures appropriate techniques for particular bird types that require specialized knowledge and equipment. We consult professionals experienced with protected species, migratory birds, and aggressive territorial species like geese and crows.
Long-term monitoring services provide ongoing assessment and adjustment of bird management strategies. We recommend quarterly evaluations, seasonal strategy updates, and population monitoring to maintain effective control over time.
Emergency response capabilities address urgent bird-related health and safety concerns that require immediate professional intervention. We maintain contacts with 24-hour wildlife services for situations involving disease outbreaks, aggressive bird behavior, and large-scale infestations.
Conclusion
We’ve covered the essential aspects of effective bird management from humane trapping techniques to innovative alternatives. The key to success lies in understanding your exact situation and choosing the right approach for your needs.
Remember that combining multiple strategies often yields the best results. Whether you opt for DIY answers or professional-grade equipment always prioritize animal welfare and legal compliance throughout your bird control efforts.
Modern technology has revolutionized bird management making it more efficient and humane than ever before. From motion-activated systems to habitat modification techniques you now have many tools at your disposal to address any avian challenge effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are bird traps and when should I use them?
Bird traps are humane capture devices designed to manage unwanted birds when other deterrent methods fail. Use them for agricultural protection, residential garden damage, wildlife management, health concerns, or bird rehabilitation. They’re effective for controlling specific bird populations without causing harm when properly deployed with appropriate permits.
Do I need permits to trap birds?
Yes, most bird trapping requires permits due to federal laws like the Migratory Bird Treaty Act. Protected species need special permits for trapping, even for agricultural damage control. Check federal, state, and local regulations before trapping. Some activities like scientific research or rehabilitation require additional documentation and reporting.
What are the most humane bird trap types?
Live traps are the most humane option, including funnel traps for small birds and drop-in traps for ground-feeding species. Mist nets are used for research but require special training and permits. These methods allow for safe capture and release without harming the birds.
How do automatic bird trap systems work?
Modern automatic systems use motion sensors, vibration detection, or timers to activate traps when birds are present. Solar-powered options eliminate external power needs and often include wireless monitoring for real-time updates. These systems reduce human intervention while maintaining humane capture standards.
Can I build DIY bird traps at home?
Yes, effective DIY traps can be made using cardboard boxes, wire cages, or plastic bottles. These cost-effective solutions use common household materials and maintain humane standards. Popular designs include simple box traps with one-way doors and funnel traps for small birds.
Where should I place bird traps for maximum effectiveness?
Position traps in active feeding areas, flight paths, and sheltered locations away from human activity. Observe bird behavior patterns and place traps near water sources or roosting sites. Avoid extreme weather exposure and ensure adequate ventilation. Strategic placement significantly improves capture success rates.
What safety precautions should I follow when using bird traps?
Check traps frequently (every 2-4 hours) to minimize bird stress. Wear protective gear when handling equipment and learn proper bird handling techniques. Position traps away from extreme weather and provide adequate ventilation. Use weatherproof covers and secure traps against wind displacement.
What are effective alternatives to bird trapping?
Non-trapping methods include visual deterrents (reflective tape, predator decoys), audio deterrents (distress calls), and physical barriers (netting, spike strips). Habitat modification through food source elimination, water restriction, and nesting site removal can provide long-term solutions without trapping.
How do I troubleshoot common bird trap problems?
For low capture rates, check bait freshness, trap positioning, and avoid human scent contamination. Fix equipment issues like door jamming or trigger sensitivity problems promptly. Protect traps from weather with covers, secure against wind, and adjust for temperature extremes and humidity effects.
What should I do with trapped birds?
Follow local regulations for captured birds – options include relocation, rehabilitation, or release depending on species and circumstances. Handle birds gently using proper techniques, provide adequate care during captivity, and document activities as required by permits. Prioritize bird welfare throughout the process.